
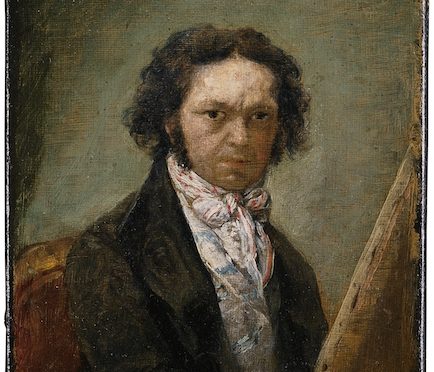
Basque Fact of the Week: Goya’s Basque Connection
Francisco de Goya y Lucientes is one of the most recognized and celebrated painters in the world. A romanticist, he is considered to be one of the greatest portraitists of his time. His paintings often depicted the reality and brutality that surrounded him, a darkness in his style that became particularly prevalent after a sickness left him deaf in 1793. His first surname, Goya, is clearly of Basque origin — the modern spelling is Goia and means “up” or “summit.” Goya is also one of my favorite painters of all time.

- Goya was born in 1746 in Fuendetodos, Aragon, though his parents were from Zaragoza, where they returned in 1749. His father, José Benito, was a gilder — someone who decorates surfaces by applying a thin layer of gold — while his grandfather was a notary, who could perform legal actions.
- Goya’s great-great grandfather, Domingo de Goya y Villamayor (originally Echeandia), was born in Zerain, in the heart of Gipuzkoa, in 1578, in the baserri Mantxolatxiki, which still stands. He was a master builder (maestro de obras) and moved to Aragon, first to Fuentes de Jiloca sometime before 1625 where he was commission to build the tower of the church, and then to Zaragoza where, ultimately, Goya’s father was born. Little is known about Domingo, other than he may have proven his nobility, by virtue of being Basque, in Valladolid in 1578. It seems that, when he moved to Aragon, he changed his maternal surname from Echeandia to Villamayor.
- Near Zerain, there is a mountain alternatively called Oa, Oamendi, or Arripillaeta which was known for its red sandstone with dark streaks. These stones were prized by stone masons, and it seems that Domingo may have learned his craft from visiting craftsmen. Several young villagers of Zerain became stone masons and craftsmen this way.
- Whether Goya himself was much aware of his Basque ancestry or not is not obvious. However, it seems that in 1792 he began the process to prove his “vizcainía,” or his Basque origins, with the goal of establishing his nobility and obtaining the privileges and rights it would provide to himself and his son. It seems he did not complete the process of proving his nobility. It’s also possible he was appealing to the nobility of his mother’s family, or both sides, when he made this request.
- However, Goya certainly included Basque elements into some of his paintings. For example, in his Portrait of the Marchioness of Santa Cruz, the lyre is decorated with a lauburu. He painted some twenty-five portraits of people with Basque origins, though many were important figures of the time and their Basque origins may have been irrelevant to him. He also painted a scene from a witches’ Sabbath, entitled El aquelarre, but that may have been a common phrase at the time and not revealing of any special connection to the Basques. In the end, whether Goya identified with his Basque ancestors is unclear.
Primary sources: Ascendientes vía paterna de Don Francisco de Goya y Lucientes; Labayru Fundazioa; Wikipedia; Museo Del Prado
Random Bits of Basqueness


The Adventures of Maite and Kepa: Part 69

Donny dismounted from his horse and walked forward until his face was illuminated by the last remaining flames of the fire. Santi had his gun at hand the whole time, not directly pointing it at the cowboy, but aiming it in his general direction. Donny seemed not to notice. The other two remained on their horses, but Kepa noticed how their hands stayed at their hips.
“My boys and I,” said Donny as he grabbed a few logs and threw them on the fire, “have been riding all day and could sure use a rest.” He looked up as he sat down next to the fire, the dancing light of the flames giving his face a menacing look. “Besides, this is our land.”
Santi shook his head. “Ez. No. We are sure not to cross in your land.”
Donny shrugged. “I’m not sure what to tell you, then. But, really, all of this land is ours, no matter what the government says.”
“That is not fair!” exclaimed Santi. “We need to live too.”
“You should have stayed in your own country, then” said Donny as he spat in the fire. “This is our country and we make the rules.”
“We don’t want any trouble,” said Kepa. “We will leave first thing in the morning.”
Santi gave him a disgusted glance but then nodded. “Yes, we will leave.”
“In the morning?” laughed Donny. “I’m sorry, but I can’t wait that long. I don’t want to spend the night here making sure you leave. I think you should leave now.”
“But, we can’t guide our horses and the wagon at night,” replied Santi. “And we have to collect the sheep.”
“Oh, are the sheep a problem?” said Donny with a wicked smile. “My boys can help with that.” He raised a hand. The other two men, who were still on their horses, dashed off toward the band of sheep that was huddled nearby, pulling their guns as they went. Soon, the night air was filled with the sounds of gunfire and the bleating of sheep.
“No!” exclaimed Santi as he started to move toward the band.
“Sit,” said Donny calmly, his own revolver pointing at the sheepherder. “Don’t make me ask again.”
Santi, pain in his face, reluctantly sat down.
“You too,” said Donny as he waved his gun at Kepa. “And don’t think I don’t remember you, boy. We have our own score to settle.”
“What did you do?” hissed Santi as Kepa sat next to him at the fire. All Kepa could do was shake his head, his hands clenched in fists to prevent them from shaking as well.
The gun shots continued as Donny stood up and walked over to the coffee pot. He grabbed a cup and poured himself the last of the bitter coffee. Taking a sip, he walked back over to his chair. “Not the worst I’ve tried,” he said as he sat.
Kepa and Santi simply glared at him, wincing each time they heard another gunshot. Soon, after more shots than Kepa could count, the shooting stopped and the other two cowboys rode back to the camp. As they dismounted and stood behind Donny, all they could hear was the dying cries of more than a few of the sheep.
“The ones we didn’t shoot ran off,” said the cowboy to Donny’s left.
Donny nodded. “Good enough.” He turned his attention back to Santi and Kepa. “And now, what about you two, eh?”
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

Fighting Basques: The other Basques of the Battle of Guadalcanal (1942): History Versus Myth
This article originally appeared in Spanish at EuskalKultura.eus on July 23, 2021.
Faced with the legend and the myth of Carranza and his group of “Basque code talkers,” the real events of those Americans of Basque origin, Basque of flesh and blood, with Basque names and surnames, have to be vindicated by Basque historiography as the actual subjects who are from our diaspora and from our common history.
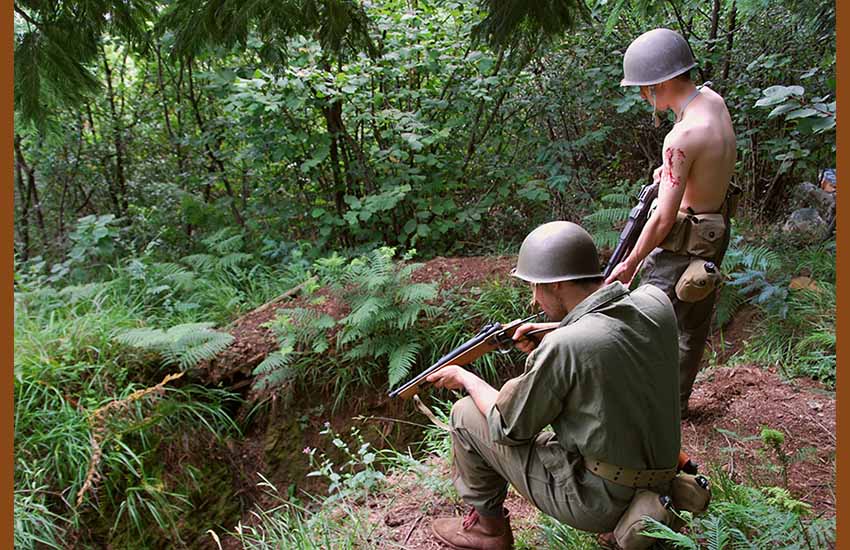

Legend tells of how the mythical captain of the United States Army, Ernesto or Frank Carranza, apparently in command of a group of sixty formidable US Marines of Basque origin – all of them the sons of sheepherders from California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada and Oregon – supposedly helped conquer Guadalcanal Island, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, in the summer of 1942.
These young men – Basque soldiers trained in broadcasting at the beginning of the Second World War (WWII) – would have carried out tasks as “code talkers” or coders, apparently using Basque as a secret code to transmit military orders, including the landing in Tulagi on August 7, 1942 and thus confuse Japanese listeners.
Decades later, on April 25, 1979, an article signed by Vicente Escudero in the Basque newspaper Deia summarized this epic under the title “110 Basques and 90 Andalusians conquered Guadalcanal in 1942.”
That article not only increased the number of Basques who, according to legend, initially took part in the battle for Guadalcanal; they were also joined by a similar number of Andalusians – we suppose that since the island was baptized as such in 1568 by the expeditionary Pedro Ortega de Valencia, a native of said Sevillian town – and revealed, strictly exclusively, the death of the enigmatic Basque-Mexican Captain Carranza on April 22, 1979 in a fatal hit-and-run in New York.
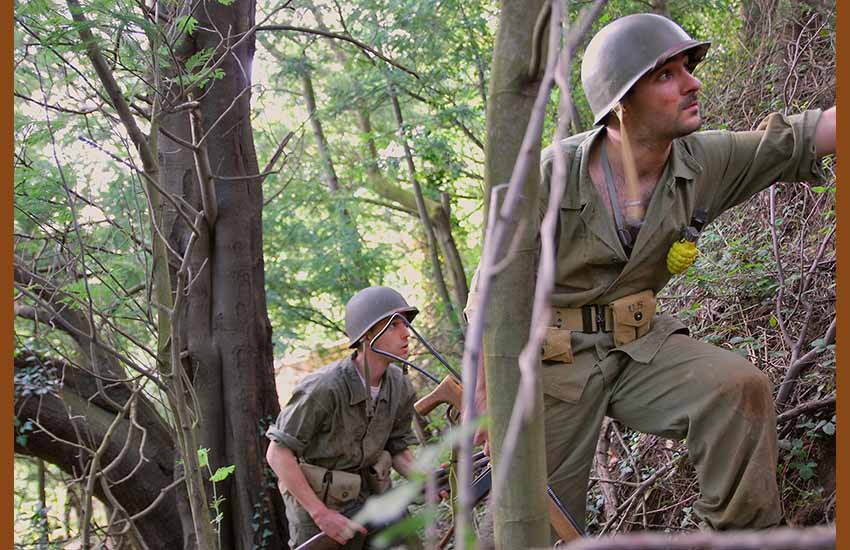

However, this legend – as fascinating as it may be – is certainly just that, a legend, a myth. With the exception of the fight that took place between the troops, mostly between American and Japanese troops for the strategic control of Guadalcanal, none of the above story is true.
If you wonder how a leading newspaper like Deia – which was joined by all kinds of publishers, including from academia, and many other media outlets in disseminating and deepening this myth for decades – took for granted the story that young Basque and Andalusian soldiers took Guadalcanal; the military use of codified Basque; the very existence of the supposed Carranza; and to make matters worse, the final notice of his death – they will discover that hoaxes, propaganda, misinformation or “fake news” were not born with Twitter.
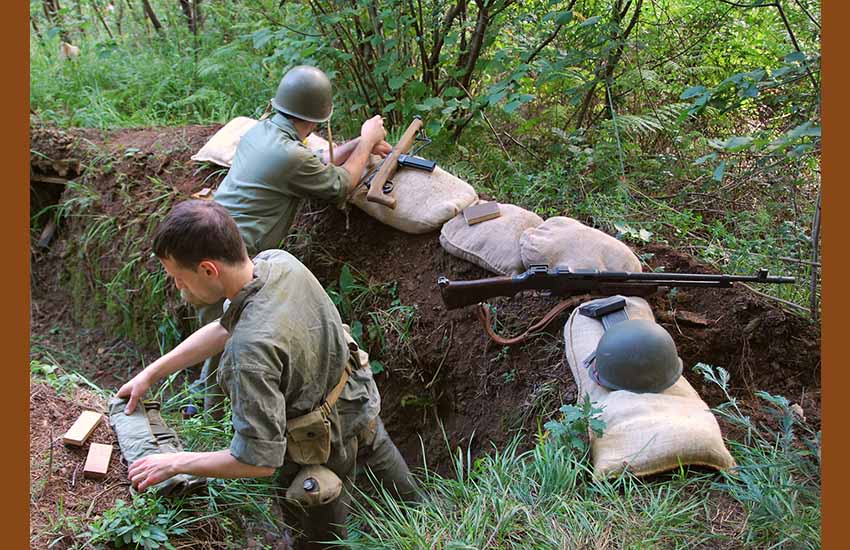

After dismantling the myth of the “Basque code talkers” a few years ago, and trying to illuminate the reasons for its birth within the framework of the relations between the Basque Government in Exile, of the Lehendakari José Antonio Aguirre, and the Office of Strategic Services of the United States, of Colonel William Donovan, it is only fair that we recognize “the other Basques,” those who did participate in the Guadalcanal Campaign, and who unfortunately were overshadowed and marginalized by the unusual myth of the use of Basque in Guadalcanal [1].
“Echoes of two wars, 1936-1945” aims to disseminate the stories of those Basques and Navarrese who participated in two of the warfare events that defined the future of much of the 20th century. With this blog, the intention of the Sancho de Beurko Association is to rescue from anonymity the thousands of people who constitute the backbone of the historical memory of the Basque and Navarre communities, on both sides of the Pyrenees, and their diasporas of emigrants and descendants, with a primary emphasis on the United States, during the period from 1936 to 1945.
THE AUTHORS
Guillermo Tabernilla is a researcher and founder of the Sancho de Beurko Association, a non-profit organization that studies the history of the Basques and Navarrese from both sides of the Pyrenees in the Spanish Civil War and in World War II. He is currently their secretary and community manager. He is also editor of the digital magazine Saibigain. Between 2008 and 2016 he directed the catalog of the “Iron Belt” for the Heritage Directorate of the Basque Government and is, together with Pedro J. Oiarzabal, principal investigator of the Fighting Basques Project, a memory project on the Basques and Navarrese in the Second World War in collaboration with the federation of Basque Organizations of North America.
Pedro J. Oiarzabal is a Doctor in Political Science-Basque Studies, granted by the University of Nevada, Reno (USA). For two decades, his work has focused on research and consulting on public policies (citizenship abroad and return), diasporas and new technologies, and social and historical memory (oral history, migration and exile), with special emphasis on the Basque case. He is the author of more than twenty publications. He has authored the blog “Basque Identity 2.0” by EITB and “Diaspora Bizia” by EuskalKultura.eus. On Twitter @Oiarzabal.
Josu M. Aguirregabiria is a researcher and founder of the Sancho de Beurko Association and is currently its president. A specialist in the Civil War in Álava, he is the author of several publications related to this topic, among which “La batalla de Villarreal de Álava” (2015) y “Seis días de guerra en el frente de Álava. Comienza la ofensiva de Mola” (2018) stand out.
Who were the real Basques of Guadalcanal?
In this article we reveal the identity of some of these true heroes, unknown until now, that we have been discovering during the progress of the “Fighting Basques” research project. The Historical Recreation Group of the Sancho de Beurko Association has joined the commemoration of the 79th anniversary of Guadalcanal and has given us their help to visualize it.
Among the “Fighting Basques” of the Guadalcanal Campaign, or “Operation Watchtower,” we find people like John Facque Elissalde, John Sallaberry Berra, Henry Etchemendy Hauscarriage, Joseph Quintana Ybáñez, Domingo Amuchastegui Guenaga, John Maitia Urbelz, John Basañez Basteguieta, James Miguelgorry Souhilar, and Joaquin Juanche Muñoz.
All of them were protagonists of “Operation Watchtower,” which lasted for six long and bloody months, from the beginning of the invasion on August 7, 1942 to February 9, 1943, approximate date of the end of the evacuation of the last Japanese troops who resisted on the island.
The Guadalcanal Campaign became the first US amphibious offensive in a new Allied military strategy to dominate the Pacific Theater of Operations. Since December, 1941, the military expansion of the Empire of Japan across the Pacific seemed unstoppable until the Allies conspired to end it. And they did so on the hitherto almost unknown Guadalcanal Island.
In January, 1942, Japanese troops had landed in the Bismarck Archipelago, located between the Solomon Islands and New Guinea. They later occupied Kavieng in New Ireland and Rabaul in New Britain in Papua New Guinea. Rabaul would become Japan’s main military base in the Southwest Pacific.
In March, the Japanese seized Salamaua and Lae in Papua and Bougainville, the largest island in the Solomon archipelago. A couple of months later, the Japanese were in Tulagi where they began the construction of a seaplane base.
Between May and July, the Japanese forces continued their expansion throughout the rest of the Solomon Islands.
On June 8, they landed in Guadalcanal, where a month later they began to build an airstrip near the mouth of the Lunga River.
For the Allies, this posed a fearsome threat against the allied air base of Espiritu Santo, located in the New Hebrides archipelago. This development also endangered the communication routes between the US, Australia, and New Zealand. It was imperative to neutralize it [2].
On August 7, 1942, 8 months after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, US Marines landed at Tulagi, Florida, Tanambogo, Gavutu, and Guadalcanal. After defeating the Tulagi and Guadalcanal garrisons, they took over the port of Tulagi and the Guadalcanal airstrip, which they christened “Henderson Field,” finishing its construction on August 21 [3].
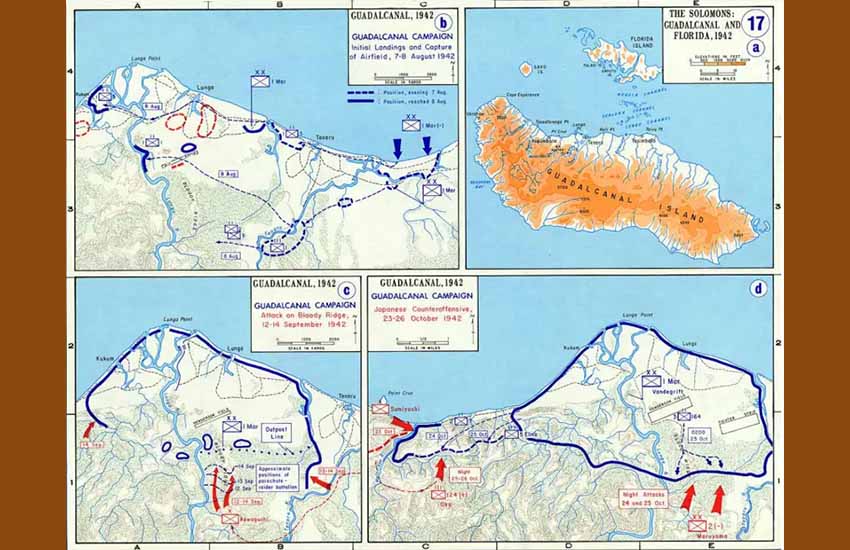
From the coast, the US fleet provided cover support for the initial amphibious assault, which came under heavy enemy air fire. On board the USS President Hayes, an attack transport, was the young Basque-Nevadan, of Nafarroa Beherean parents, John Facque. The mission of the USS President Hayes was to land units of the 2nd Marine Regiment on the northeast side of Guadalcanal.
On the ground, among the marines of the Second Division we identified the Basque-Nevadan Henry Etchemendy. Etchemendy, also of parents from Nafarroa Beherea, served in the 10th Regiment, providing artillery support from the beginning of operations.
The Guadalcanal Campaign had just begun, leading to numerous land and naval battles over the coming months, with significant aerial skirmishes.
From Rabaul, the Japanese launched air strikes against the American forces deployed in Tulagi and Guadalcanal, which were joined by attacks by the destroyers and light cruisers of the Imperial Navy, while supplying their troops on the ground as best they could.
The shortage of food and military materials would be a general trend for both the Allies and the Japanese, although it would be noticed with much greater impact among the Japanese troops.
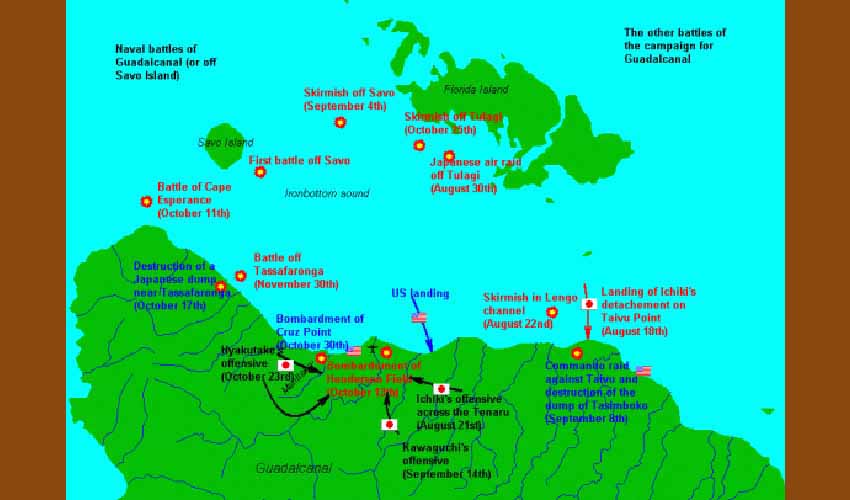
The clashes between Japanese and American patrols were constant, while sporadic Japanese attacks of greater magnitude took place, such as the one that occurred between October 23 and 26, 1942, which aimed to recover the airstrip now known as “Henderson Field.”
Among the American reinforcements sent to Guadalcanal during the beginning of autumn, there was, for example, the light cruiser USS Boise. On board we find Joseph Quintana – born in 1917 in Nevada to Nafarroan parents. The mission of the USS Boise and the soldiers like Quintana was to give cover during the landing of a new wave of marines in Guadalcanal.
The USS Boise was damaged during the Battle of Cape Esperance on the night of October 11-12 and would have to return to the US for repairs. Quintana passed away in Sacramento in 1979.
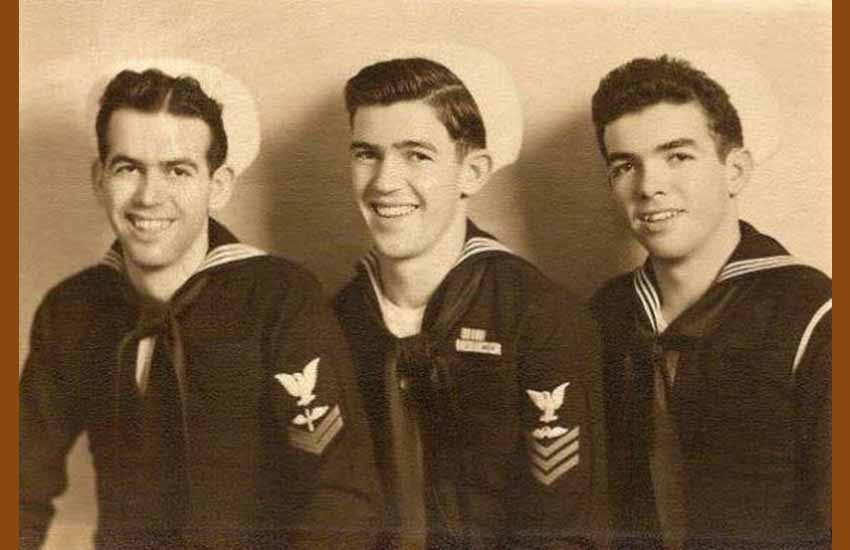

The USS Boise was joined by the escort carrier USS Copahee, which moved fighters and torpedo boats bound for “Henderson Field.” Domingo Amuchastegui, born in 1923 in Nevada to Bizkaian parents, served aboard the Copahee, where he was in charge of repairs to the structure of embarked aircraft.
John Maitia, a Marine of the 14th Aircraft Group, landed on the island in October 1942.
Maitia, whose father was from Nafarroa Beherea and whose mother was from Nafarroa, was born in California in 1922. He took part in the so-called Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, another attempt (again unsuccessful) to retake Henderson airfield, with an important deployment of the Japanese Navy and a large number of Japanese troop reinforcements from Rabaul.
The reinforcements sent by the Americans to repel this new counteroffensive were attacked by Japanese airplanes on November 11 and 12.
The naval battle was a victory for the Allied side after days of heavy fighting, ending on November 15.
It was Japan’s last and greatest attempt for “Henderson Field.”
Maitia passed away in 2018 at the age of 95.
The marine Facque was aboard the cruiser USS Northampton when it was sunk by Japanese torpedoes at the Battle of Tassafaronga on November 30, 1942, in an effort to prevent the Japanese from reinforcing their troops at Guadalcanal. Facque was unharmed and survived the sinking.
He died in 2015, at the age of 93.
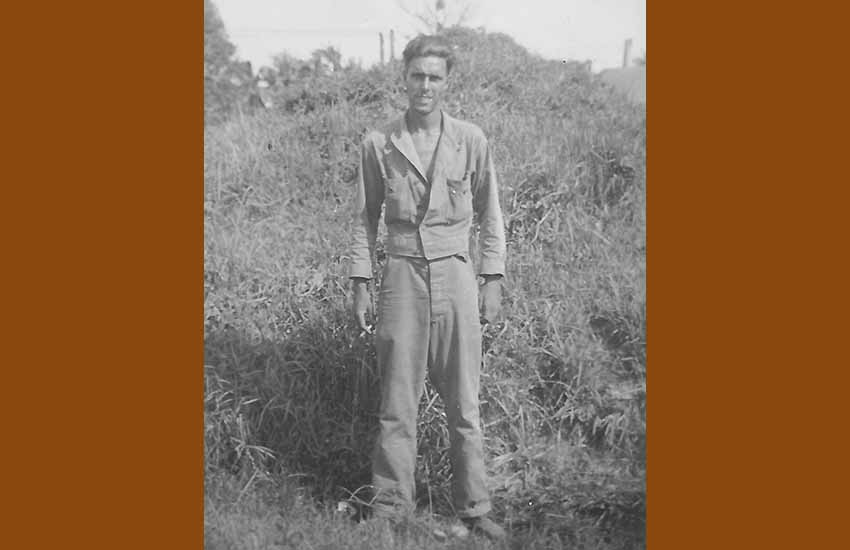

In December, 1942, two other Basque-Californians arrived at the Guadalcanal front: the soldier John Basañez and the “seabee” James Miguelgorry. Basañez, of Bizkaian parents, served in the 185th Regiment (Regimental Combat Team) of the 40th Infantry Division, facing Japanese troops from the first minute. At Guadalcanal he fell ill with malaria, which he carried for the rest of his life. He passed away in South San Francisco in 2001.
Miguelgorry was born in 1918 to parents from Nafarroa Beherea. He served in the 18th Naval Construction Battalion, which was assigned to the Second Marine Division, for reconstruction duties. Miguelgorry’s unit was outfitted with Marine uniforms and equipment. He passed away at the age of 81 in Washington State.
At the beginning of 1943, the Marine of the Second Division, John Sallaberry, and the soldier of the 161st Infantry Regiment, Joaquín Juanche, arrived at Guadalcanal. The Basque-Californian Sallaberry, of a Lapurdian father and a Gipuzkoan mother, served with the 6th Regiment, which disembarked from the USS President Adams in the Guadalcanal-Tulagi area. Juanche, born in California in 1915 to Nafarroan parents, was involved in bloody fighting in defense of the positions around “Henderson Field.” He also participated in the elimination, from January 10 to 21, of a concentration of Japanese troops in what became known as the Matanikau River Pocket, a dense redoubt of jungle situated between a steep hillside and a high cliff above the Matanikau River.
Like Etchemendy, his compatriots Sallaberry and Juanche also fought until the end of the Guadalcanal Campaign.
From January 10 and for about two weeks, the US troops began an offensive to eliminate the Japanese forces from the island, in which the 161st of Juanche participated very actively.
Sallaberry will obtain the Silver Star for his heroism in an action that took place on January 21 in Guadalcanal.
During a patrol with his platoon several hundred meters beyond their defensive lines, an enemy machine gun wounded one of his comrades. Sallaberry, with the help of another marine, picked up the wounded man under constant enemy fire and without regard for his own safety. After Guadalcanal, Sallaberry, Etchemendy and Juanche, together with their comrades in arms, would continue the fight in the southwestern Pacific.
Sallaberry passed away in 1990 and Etchemendy in 2001.
Unfortunately, Juanche was killed in combat at the age of 27 on August 5, 1943 in New Georgia.
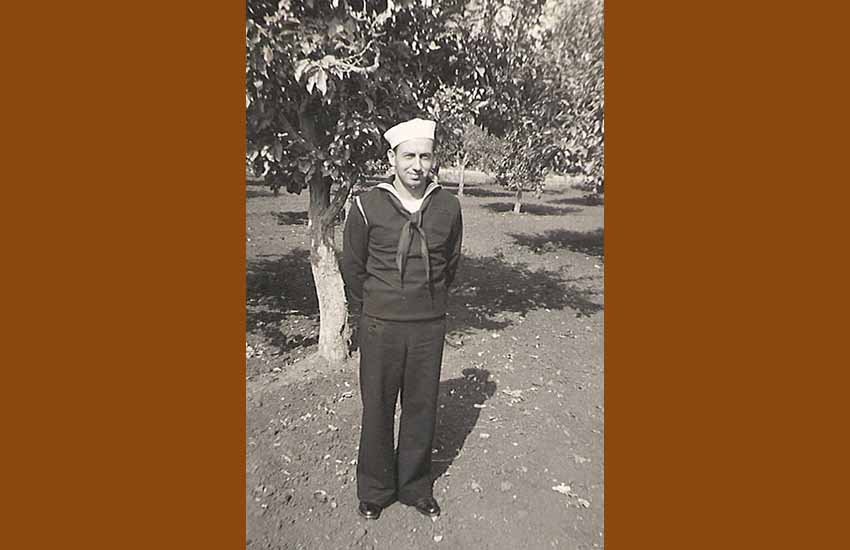

The losses, both human and material, were substantial for both sides, although evidently the balance turned to the Allies. About 30,000 Japanese soldiers out of a total of 36,000 perished in the Guadalcanal Campaign, most of them as a result of famine and tropical diseases.
After Guadalcanal, Japan found itself on the defensive for the first time since Pearl Harbor, unable to replace the air and sea fleet destroyed during the long Guadalcanal Campaign.
The allied counteroffensive continued through the rest of the Solomon Islands and New Guinea, capturing Japanese bases of enormous strategic importance, which would facilitate success in future campaigns in the southwest and central Pacific.
The historical narrative presented here arises from verifiable evidence and imposes itself on the myth and its undeniable power of seduction, which to date had falsely connected the Basque with the remote island of Guadalcanal during WWII, masking the true events carried out by Americans of Basque origin, of Basque flesh and blood.
The legend of Carranza and his group of “Basque code talkers,” and its promoters in the shadows, are left with as their only refuge the passing of time, the forgetting of history as it happened and its true heroes.
These heroes must be reclaimed. Facque, Sallaberrry, Etchemendy, Quintana, Amuchastegui, Maitia, Basañez, Miguelgorry and Juanche – among others that our investigation can still reveal – must be indisputably vindicated by Basque historiography as active subjects of our diaspora and of our common history.
We owe it to them and to their memory if we want history to impose itself on myth.
Thus, is necessary more than ever to create a future with memory; a public, didactic and inclusive memory.
Notes
(1) Oiarzabal, Pedro J. and Guillermo Tabernilla. “El enigma del mito y la historia: ‘Basque code talkers’ en la Segunda Guerra Mundial. La OSS y el Servicio Vasco de Información—la Organización Airedale”. Saibigain, No. 3 (2017)
(2) Mueller, Joseph N. (1992). Guadalcanal 1942: The Marines Strike Back. Oxford: Osprey Publishing
(3) Danny J. Crawford, Robert V. Aquilina, Ann A. Ferrante, Lena M. Kaljot, and Shelia P. Gramblin. (2001). “The 2nd Marine Division and its Regiments”. Washington D.C.: History and Museum Divisions Headquarters, U.S. Marine Corps
Collaborate with ‘Echoes of two wars, 1936-1945.’
If you want to collaborate with “Echoes of two wars” send us an original article on any aspect of WWII or the Civil War and Basque or Navarre participation to the following email: sanchobeurko@gmail.com
Articles selected for publication will receive a signed copy of “Combatientes Vascos en la Segunda Guerra Mundial.”
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

Basque Fact of the Week: The “Butter Buns” of Bilbao
When I visited my dad’s family in Munitibar, I’d stay with his brother Martin and his wife Rosario. They ran the Herriko Taberna. Each morning, after I woke up, I’d make my way to the bar. Rosario was already hard at work, cleaning the bar and preparing the days meals. I’d take my seat at the bar and she’d serve up a cafe con leche and a pastry. I never really gave it much thought, but those pastries stayed with me, their subtle sweetness and simplicity perfect for starting the day. It was only much later that I realized their unique place in the life of Bizkaia.

- Bollos de mantequilla, as they are called, are actually a quite simple pastry. Essentially, they are a Swiss bun or brioche, cut in two and filled with a cream made from butter and eggs. They often have a sprinkling of sugar on top. They have a very soft texture and only a hint of sweetness.
- Their origin dates back to 1813. That was the year that two cousins from Switzerland, Bernardo Pedro Franconi and Francesco Matossi, came to Bilbao. According to one story, they were trying to sell goats milk. Whatever the case, they eventually set up a pastry shop in the old part of town – the Casco Viejo – at Calle Correo nº 2 to be precise. Years later, they opened a second shop in the Plaza Nueva. It wasn’t long before they had a franchise that reached across Spain, with some 50 shops in cities such as Burgos, Santander, Pamplona, and Madrid.
- The cousins started making milk buns, or brioches, which became known as Swiss buns. But it wasn’t until they added that butter cream filling that the bollo de mantequilla was born that is now so ubiquitous in Bizkaia. Today, you can find shops all over Bilbao that serve these simple delights; BilbaoClick lists several you can check out next time you are there.
- However, if you can’t make it to Bilbao any time soon, you can always make your own! You can find recipes for bollos de mantequilla all over the internet, but Bake Street provides not only a good recipe but also advice on making them. The ingredients are pretty simply – water, flour, sugar, butter, milk, eggs, yeast, and salt – but they can take a few days to make, due to the time the buns need to rise.
- BilbaoClick gives another history of these pastries, though their story also starts on Calle Correo nº 2. According to them, the owner of the shop “Café Suizo” traveled to Switzerland in 1831, where he discovered the bun filled with butter cream. He brought it back to his shop and Bilbao where it quickly became an enormous hit.
Primary sources: Bollo de mantequilla, Wikipedia; Bollos de mantequilla from Bilbao, Bake Street; El bollo de mantequilla, Conoce Bilbao con Esme; Los 9 Mejores Bollos de Mantequilla de Bilbao, BilbaoClick
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

The Adventures of Maite and Kepa: Part 68

Months passed and Kepa had still seen no sign of the zatia. He had resigned himself to his routine of tending the camp. The only reprieve was when Dominique stopped by with supplies. The two of them had struck up a genuine friendship. To be honest, Dominique was the first iparraldetar that Kepa had really gotten to know. For how small the Basque Country was, he had never really made much of an effort to get to know the other parts. He vowed to himself to visit the baserri that Dominique was from when he got back home.
If he got back home, he corrected himself. Without the zatia, there was no way to return home, and he was starting to seriously doubt if they would ever find it. He couldn’t imagine that he and Maite had been sent here without reason, but he couldn’t see the purpose in him living this hellish life, alone in the mountains.
One day, when he had finished his daily chores and was a bit more restless than normal, he wandered into the nearby aspens. The smooth tall trees seemed to reach to the heavens, and the sun sparkled through the gently swaying leaves, dappling the ground with a tapestry of moving shadow. It took him a moment to notice the strange markings on the trees. He looked at the nearest tree a bit closer. Bai! They were carvings, left by previous herders who had passed this way. The closest tree had a carving of an elegant church, outlined in crude knife cuts that, together, conveyed a beauty that Kepa wouldn’t have thought possible. He circled the tree, only to find another carving, this one of the torso of a naked woman. Underneath was a simple inscription: “Pedro hemen zegoen” — “Pedro was here.” Kepa examined the other trees. Many had similar markings while some had notes left behind for other herders. One inscription, written in Spanish, said “If this life is what those damn oldtimers told me, my balls are carnations.” Kepa just shook his head and suppressed a resentful chuckle. He knew exactly how that man had felt.
Before he went back to the camp, Kepa pulled out his own knife. Finding a blank canvas, so to speak, he carved his own inscription. “Kepa hearts Maite.” He smiled, but then realized that, if they did find the zatia, this, along with everything he had done, would disappear with the pop of the time bubble. He shook his head and wandered back to the camp.
It wasn’t long before evening came and Santi came with it, his dog by his side. The ever laconic Santi simply nodded as he sat down near the fire and Kepa handed him a bowl of stew. Kepa didn’t say anything, but inwardly sighed, wishing for some meaningful human interaction. But, as had happened so many nights before, Santi finished his meal in silence and then handed the bowl to Kepa to wash as he prepared to sleep.
Santi was rolling out his bedroll in the dying light of the fire while Kepa gathered his own bowl to wash in the morning when they heard the clip-clop of horses. Santi moved toward the wagon and grabbed his shotgun while Kepa stood next to him, waiting to see who their visitors were. In the months Kepa had been in the hills with Santi, this was the first time they had gotten any visitors so late at night and Kepa was more than a little scared.
Three figures rode up, their features obscured by the shadows. That the moon was waxing crescent meant that there was little light. The horses stopped as they got to the edge of the camp.
“Nor da?” barked Santi, his gun raised slightly, not pointing at the men directly, but clearly showing that Santi wasn’t messing around. “Who’s there?”
The man on the lead horse, who seemed to sit up a bit straighter than the others, his large shoulders visible in the darkness, just chuckled. “Calm down, you damn Basquo. We’re just friends, hoping to get a brief respite from a long day of riding.”
Kepa shivered as he recognized that voice. It belonged to Donny McCown.
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

Basque Fact of the Week: Cristina Iglesias and Her Newest Creation, Hondalea
Donostia, the capital of Gipuzkoa, is a city filled with a myriad of things to see and do. From the Parte Vieja, where one can wander all night sampling pintxos, to the wonderful beaches, to the history of the San Telmo museum, there is so much to do. And, thanks to Cristina Iglesias, a sculptor native to the city, there is one more attraction that will certainly become a must-see on any visit to the city: Hondalea.

- Cristina was born on November 8, 1956, in Donostia to Eduardo Iglesias Hernández and Maritxu Fernández-Berridi Lecuona. Cristina is one of five children, all of whom became artists and creators of one type or another. She began studies at the University of the Basque Country in chemical sciences, but began down a path of art that took her to the Chelsea College of Arts in London.
- Cristina’s career grew in the 1980s and really took off in the 1990s. Her first solo exhibition was in Portugal in 1984 but this was soon followed by exhibitions across Europe, in Vienna, Bordeaux, Athens, Dusseldorf, and Ghent. The 1990s saw her reach across the ocean with exhibitions in Canada, the United States, and Australia. In 1999, she was awarded the Premio Nacional de Artes Plásticas, for having opened new paths in the plastic arts (sculpture for example). That year, she also created special pieces designed for the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao. Today, her work can be found in some of the most prestigious museums in the world, including the MACBA (Barcelona), the Tate Gallery (London), the Reina Sofía Art Center (Madrid), and the MoMA and the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museums (New York). In 2016, she was awarded Donostia’s Tambor de Oro. And, in 2020, she won the Royal Academy Architecture Prize in London for looking “at the spaces between buildings, creating thoughtful work that rewards sustained reflection.”
- Her work incorporates multiple materials, fusing the industrial and organic. She explores our relationships with both nature and space. One of her works, Deep Fountain, looks almost like a marsh with organic green leaves that cover the bottom of a pool. As the pool fills from a crack, or abyss, in the center, the water slowly flows over the sculpted leaves.
- With her most recent work, entitled Hondalea (Marine Abyss in Basque; check out the video, the photo doesn’t do it justice) and unveiled in June 2, 2021, Cristina has converted an abandoned lighthouse on the Basque coast into a kinetic water sculpture. The lighthouse, on Santa Klara Island in the middle of Donostia’s bay, has been completely transformed. The bottom was excavated and replaced with bronze sculpture that mimics the rugged Basque coastline. Water flows in and out, driving by hydraulics, that mimic the crashing of the waves. All of this is surrounded by the walls of the lighthouse itself.
Primary sources: Cristina Iglesias, Biografias y Vidas; Cristina Iglesias, Wikipedia; Cristina Iglesias, Guggenheim Bilbao; Barandiaran Múgica, Arantza. Iglesias, Cristina. Enciclopedia Auñamendi. Available at: https://aunamendi.eusko-ikaskuntza.eus/es/iglesias-cristina/ar-52092/; Harriet Lloyd-Smith, Cristina Iglesias turns derelict lighthouse into staggering geological sculpture, Wallpaper*.
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

The Adventures of Maite and Kepa: Part 67

The next few weeks at the boarding house seemed a blur. Every day was the same: get up, have a quick bite and some coffee, prepare breakfast for the boarders, clean the rooms, prepare lunch, and take a small break before having to get ready for dinner. Most of the faces were the same, and Maite was getting to know some of them pretty well. However, there was always a new face or two, someone popping in for a meal or a camp foreman who was in town gathering supplies. While Maite didn’t love the daily grind of the boarding house, she got to enjoy all of the characters that gave the house life.
She still hadn’t had any luck finding the zatia. She was convinced it wasn’t in the boarding house, but if it wasn’t there, she had no clue where it might be. Why was there a time bubble here if there was no zatia? And, if they never found the zatia, would they be stuck here for the rest of their lives? Maite didn’t know of any other way to pop the bubble and return to her own time.
It was early Friday morning and Maite was sitting at the table, enjoying her small breakfast and cup of coffee when Juan Jose walked in. He wasn’t normally up this early, so his presence startled Maite.
“Juan Jose! What are you doing up so early?”
The old man shrugged. “Just couldn’t sleep. My mind kept drifting back to the Basque Country and wouldn’t leave.” He sighed. “Mind if I join you?”
“Not at all,” said Maite as she waved to the seat across the table from her. “Let me get you a cup of coffee,” she added as she stood up. “Want anything to eat?”
“Ez, not yet. My mind is awake, but my belly is still alseep.”
Maite laughed as she brought Juan Jose a cup of coffee. “Extra milk and sugar, the way you like it.”
Juan Jose smiled. “Eskerrik asko.”
“Any big plans for the day?” asked Maite as she sat down again.
Juan Jose laughed. “You mean, besides trying to strike up a game or two of mus, like every other day? No, not really.”
“When was the last time you went home, went to the Basque Country?”
Juan Jose sighed again. “Too long. Like I told you before, I went back a few times not long after I first got here. I had a girl back home. The first time, I tried to convince her to come out here, that life was pretty good over here. But, the second time, she was already married. She didn’t want to come here and she got tired of waiting for me to come back.” Juan Jose took a sip from his cup and looked at Maite. “You know what hurt the most? The guy she ended up with, he was my best friend when we were kids. We were supposed to come out here together, become rich together. But, he got scared in the end and didn’t come. And he ended up with my girl.” Juan Jose shook his head as he looked down into the swirls of his coffee. “I probably should have stayed too.”
Juan Jose cleared his throat, took a sip, and looked up. “Anyways, what about you and that young man? What are your plans?”
Maite blushed. “We aren’t sure yet. We just want to get past this little adventure and then see what life has for us next.”
“Kontuz! Be careful! This ‘adventure’ as you call it has a way of keeping people trapped and not letting go. There’s another boarding house down the road… one of the boarders has been there for fifty years, if you can believe it!”
“Fifty years? Just living in one of these small rooms?”
“Hell, I’ve been in mine for ten years now. It’s not much, but it is comfortable, the people are good, and they keep you fed. And I can always find a card game.”
Maite shook her head. “No offense, but we hope to move on as soon as possible. Find the next adventure and all that.”
“I don’t blame you. When I was young, I was always looking for the next adventure. I never thought I’d be here, that’s for sure.”
Maite swallowed the last of her coffee. “Well, I better get working on breakfast. It’s been nice talking with you, Juan Jose.”
“Berdin,” replied the old man as his gaze returned to the dark pools of his coffee cup.
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

Basque Fact of the Week: Basque Athletes at the Paralympics
The Olympics ended a few weeks ago, and now it’s time for the Paralympics, which start on Tuesday. The first official Paralympic Games were held in 1960 in Rome, though there were precursors to this historic event. There are at least thirteen athletes from the Basque Country going to Tokyo for the 2020 Paralympic Games. They will be competing in events from wheelchair basketball (both men’s and women’s), swimming, rowing and paracanoe, running, cycling, triathlon, table tennis, and archery.

- Agurtzane Egiluz Ibarguen was born in 1997 in Vitoria, Araba. At the age of 14, she was injured in a bus accident. She is on the Spanish national wheelchair basketball team. She is studying for a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration and Management at the Faculty of Economic and Business Sciences the University of the Basque Country.
- Beatriz Zudaire Garcia is also on the Spanish national wheelchair basketball team. From Pamplona, Nafarroa, she began as an accomplished swimmer, but switched to basketball when a team was formed in Vitoria.
- Asier García Pereiro is on the men’s Spanish national wheelchair basketball team. He was in an accident when he was 13. In addition to playing basketball, he graduated with a degree in computer science from the University of Deusto. He is the captain of the team.
- Iñigo Llopis Sanz is from Donostia. He is a swimmer, specializing in the 100 meter backstroke and the 400 meter freestyle. He is also passionate about soccer and has plans to become a coach.
- Nadia Zudaire Borrezo is also a swimmer, from Zubieta, Gipuzkoa, who will compete in the 400 meter freestyle. In the Berlin Swimming Championship held in July, she set Spanish records for both the 400 and 800 meter freestyle.
- Higinio Rivero Fernandez is a specialist in the paracanoe. In 2013, he had an accident while climbing that left him paraplegic. He kept his same passion for sport, but channeling it instead into canoe.
- Jorge Pineda Matabuena is a rower from Getxo. He will compete in the four-crew mixed boat. In this race, the crew must be composed of two men and two women. In addition, two must be physically disabled and two visually impaired, accompanied by a non-disabled helmsman.
- Estibaliz Armendariz Zubillaga, born without her right leg in Pamplona in 1974, is a rower. She is also an R&D manager for Naitec. She also translated Lawrence Kraus’s The Physics of Star Trek to Spanish.
- Izaskun Osés Ayúcar was also born in Pamplona, in 1984. She is a blind runner, having won bronze in the 2016 Rio Games in the 1500 meters. She earned a nursing degree but had to give up the profession due to her deteriorating vision.
- Eduardo Santas Asensio, born in Zaragoza but living in the Basque Country, is a cyclist. Since 2014, he has won 14 medals at the World Championships for Adaptive Cycling. He won a bronze medal in the Mixed Team Spring in the 2016 Rio Games.
- Rakel Mateo Uriate is a paratriathlete. One of her legs was paralyzed after an accident in 2001. She has been the Spanish paratriathlete champion three times in her career. She is currently ranked 5th in the world. She is from Mungia, Bizkaia.
- Iker Sastre Sanchez-Vallejo was born in Bilbao in 1977. His sport is table tennis. When he was 23, he suffered a surfing accident that left him with a spinal cord injury. He has won multiple championships in Bizkaia, Euskadi, and Spain. He is currently ranked 9th in the world. He is the first Basque table tennis player to ever play in the Olympics in any form.
- María Carmen Rubio Larrion is an archer from Pamplona. She was born in 1961. She participated in the 2012 Games in London. She got her start in her archery career thanks to a scholarship from cycling legend Miguel Induráin.
Primary sources: BasqueTeam; Trece deportistas vascos participarán en los Juegos Paralímpicos, EiTB.eus
If you get this post via email, the return-to address goes no where, so please write blas@buber.net if you want to get in touch with me.

