My dad was from Munitibar-Arbatzegi-Gerrikaitz. My friend — and distant cousin — Jon Zuazo sent me this video, made by Karmelo Goikoetxea. It is simply spectacular. It must have been hard for the men and women who, like my dad, had to leave this behind…
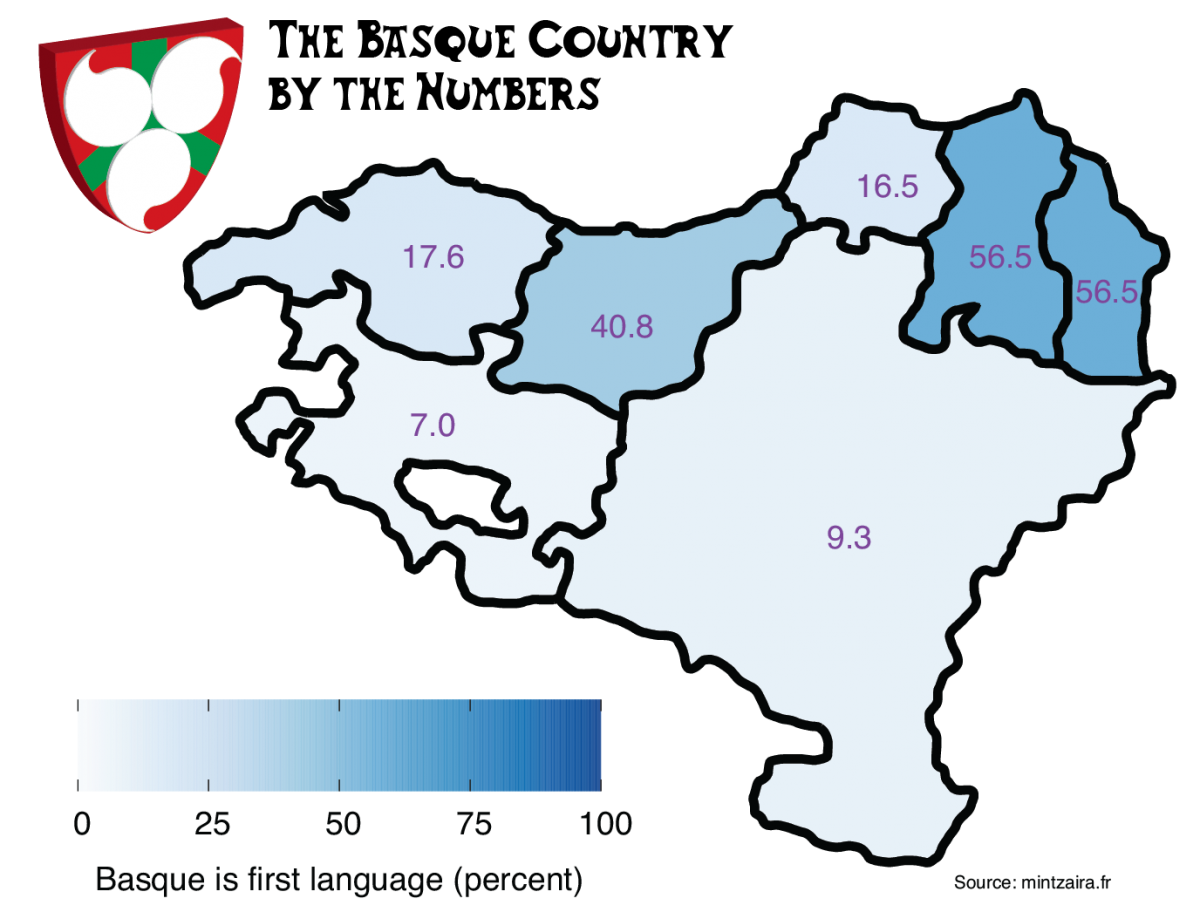
The Basque Country by the Numbers

The percent of people who have Euskara as their first language. The numbers for Zuberoa and Nafarroa Beherea are shared. Source: https://www.mintzaira.fr/fileadmin/documents/Aktualitateak/015_VI_ENQUETE_PB__Fr.pdf

Buber’s Basque Story: Part 7
It was about nine thirty in the morning when Maite’s little Fiat pulled up again outside of Goikoetxebarri, the baserri where Kepa lived with his mom.
“Mil esker for the ride,” said Kepa over a repressed yawn as he opened the door. “Are you sure you don’t want to crash here for a while, before driving home? If you are as tired as I am…”
“And sleep in that creepy room with those pictures of your uncle?” Maite replied, shaking her head. “No thanks.”
Buber’s Basque Story is a weekly serial. While it is a work of fiction, it has elements from both my own experiences and stories I’ve heard from various people. The characters, while in some cases inspired by real people, aren’t directly modeled on anyone in particular. I expect there will be inconsistencies and factual errors. I don’t know where it is going, and I’ll probably forget where it’s been. Why am I doing this? To give me an excuse and a deadline for some creative writing and because I thought people might enjoy it. Gozatu!
Kepa did have to admit that the middle room was a little creepy. His ama insisted that they keep the photos of his aita’s uncle, Domingo, up on the wall. Domingo had died fighting for the Republicans during the Spanish Civil War as Franco’s forces had sieged Bilbao, and the family had always honored his sacrifice by having many photos of the then-young man around the house. They had all gotten consolidated in the middle bedroom upstairs and now the shrine to his great uncle gave the room a very disturbing atmosphere.
“Fair enough,” Kepa said. “But, at least come in for a coffee. I’m sure ama saw us drive up and already has a glass ready for you.”
Maite smiled in defeat. “Ados,” she said as she turned off the engine and got out of the car.
The smell of coffee filled their senses as they passed the foyer into the small kitchen.
“Egun on!” said Kepa’s ama as the two entered the kitchen. She placed two glasses of coffee on the small table, beckoning them to sit. The table was already filled with cookies and biscuits.
“How are the fish, Mari Carmen?” asked Maite as she took a seat at the table.
Ever since they were children, Maite had always asked Kepa’s ama, Mari Carmen, about her fish. She and her parents had come to dinner at the baserri one night and Mari Carmen had served the best fish Maite had ever tasted. She had assumed that Mari Carmen must have a personal pond full of the best and freshest fish in the Basque Country and ever since she had asked Mari Carmen about her wonderful fish. Even when she grew older, she kept the conceit going as an inside joke.
Mari Carmen smiled. “The fish are wonderful, as always. How was the fiesta?”
“It was great,” said Kepa as he shoved a few of the cookies into his mouth and took a sip of his coffee. “Koldo’s new band is really good. They have some excellent songs and all of them are great musicians. I think they could do really well.”
Maite nodded enthusiastically. “I agree. They’re better than all of the other new bands I’ve heard and better than most of the ones that are on the radio. They are really talented.”
“Pozik nago,” replied Mari Carmen. “I’m glad Koldo has finally found his place.”
Kepa knew what she meant. Koldo had struggled to really find his footing as an adult. He had tried various jobs, working at one of the factories, taking classes to be a mechanic, tending bar, but nothing had stuck. He seemed to only be happy when making music.
Maite finished her coffee and stood up. “Well, I better go. Thanks for the coffee Mari Carmen.”
“Ez horregatik, neska. Ondo ibili,” replied Mari Carmen.
Kepa walked Maite out to her car. “Thanks again for the ride. I really appreciate it. And sorry for being so grumpy at the beginning.”
Maite laughed. “If you weren’t grumpy, you wouldn’t be Kepa.”
Kepa leaned in to give Maite a kiss on each cheek, but Maite grabbed his head and planted a kiss on his lips. “Ikusi arte,” she said with a devious smile.
Kepa just stood there, befuddled, as Maite drove off.

Basque Fact of the Week: The Summer Solstice
The summer solstice, being the longest day of the year, is an important event in many cultures, marking the changing of seasons. Because of its importance, elaborate rituals and rites have arisen around this date all around around the globe, and the Basque Country is no exception. Many of the pre-Christian elements have been confused and combined with Christian holidays, as the Church placed San Juan’s Feast near the Summer solstice. That said, the echo of many elements of pre-Christian celebrations can still be heard.

- Of particular importance is the bonfire. On the day of San Juan, bonfires were lit in front of homes, in plazas, at crossroads, and at any other prominent place. This bonfire had healing properties, conferred to it by the herbs that had been collected throughout the year to help start the bonfire.
- This bouquet was created the previous year, on the eve of San Juan, by the women of the house. They collected lilies, roses, carnations, daisies, an ear of wheat, a corn plant, and a branch from a cherry or apple tree with its fruit. It also contained many herbs, things like laurel, fern, wormwood, celery, and rosemary. This bouquet was blessed at Mass this year to be ready for next year to start the bonfire.
- The bouquet itself had many of its own healing properties. It protected from thunder, relieved toothaches, softened cows udders, and drove away snakes. The mist of a cooked bunch from the bouquet fought phlegmon. To cure a chest cough, one took a foot bath in hot water after boiling in it a bundle of the bouquet. To cure the evil eye, the damaged part was washed with a small cloth.
- To benefit from the healing properties of the bonfire itself, one had to jump over it at least three times and chant special spells, such as one heard in the mountains of Nafarroa: “Ogia Espainara, ezkabia Frantziara” (Bread to Spain, scabs to France). Precisely at midnight, people burned olive leaves, as this eliminated warts, cysts and other skin malformations. People saved the ashes from the bonfire as they had their own healing powers.
- One odd ritual, practiced in the Basque Country and more widely in Europe, related to herniated children. To cure the children, two men would pass the child through an opening they had made in a young tree. They would cut a slit in the tree and pry it open for the child to be passed through several times. If the tree recovered once it was reformed, the child would be healed.
- Water also achieved special healing powers on this day. If people took a pre-dawn bath in special streams or fountains, or even in the dew in certain fields, they would benefit from the healing properties of the water.
- Finally, if you slept in on San Juan’s day, you would be sleepy all year. But, if you got up early on the longest day, you would sleep easily the rest of the year.
Primary source: Aranburu Urtasun, Mikel. Solsticio. Enciclopedia Auñamendi, 2020. Available at: http://aunamendi.eusko-ikaskuntza.eus/es/solsticio/ar-109287/
Back to normal… I hope!
I think I’ve gotten things working normally again. Hopefully there will be no more glitches for the foreseeable future. If you see anything odd, please tell me.
Best, Blas
Ugh. Some issues with Buber’s Basque Page
Dear visitor. You may have noticed some issues with Buber’s Basque Page, particularly regarding how it is been up and down today and how some images are broken. I think there is something corrupted in my WordPress install. I will probably have to reinstall it at some point, which might mean I go dark for a little while. I’ll try to do this soon and as seamlessly as possible.
If there are any WordPress experts out there who might be willing to give me some advice, I would welcome it.

Buber’s Basque Story: Part 6
Kepa passed a red plastic cup to Koldo. “Kalimotxo, ezta?”
Koldo nodded as he took the cup. “Mil esker!”
“That last song was… different,” said Kepa, taking a sip from his own cup. “Don’t get me wrong, I really liked it, but sorginak? Madarikazioak? Curses? Where did you come up with that stuff?”
Koldo shrugged. “That one was all Ainhoa. She wrote that song, music, lyrics, everything.”
Kepa looked at her. “Well?” he asked. “What’s the story?”
Buber’s Basque Story is a weekly serial. While it is a work of fiction, it has elements from both my own experiences and stories I’ve heard from various people. The characters, while in some cases inspired by real people, aren’t directly modeled on anyone in particular. I expect there will be inconsistencies and factual errors. I don’t know where it is going, and I’ll probably forget where it’s been. Why am I doing this? To give me an excuse and a deadline for some creative writing and because I thought people might enjoy it. Gozatu!
Ainhoa smiled as she took a drink. “My mom was born in Nafarroa, in Zugarramurdi, though her family moved to Bizkaia when she was young. She told me a story about some ancestor of hers, or rather, the sister of one of her ancestors. It seems that this sister was one of the healers of the village, and some said she had supernatural powers. When the Inquisition came to town, some of her neighbors, probably jealous or something, accused her of sorginkeria, of witchcraft. The Inquisition tried her and when she refused to recant, they burned her at the stake in the auto de fe in Logroño.” Ainhoa shrugged. “I thought it would make a cool story for a song.”
“That is so cool!” exclaimed Itxaso. “Did she really curse everyone?”
“Who knows?” answered Ainhoa. “We don’t know anything more about her. She was killed over four hundred years ago. Hard to know what really happened back then. I just made up the curse for the song.”
“I bet she really did curse them,” said Itxaso in an excited whisper. “That’s what I would have done, anyways.”
“You don’t really believe in this stuff, do you?” asked Maite incredulously.
Itxaso shrugged. “Who knows, science girl? ‘Izena duen guztiak izatea ere badauke — Everything with a name exists.’ Not everything can be explained in your books.”
“‘Izenak ez du egiten izana — A name does not make something true’,” responded Maite. “I need more proof than just a story to believe it.”
Koldo held up his cup as if to toast. “It doesn’t matter to me if it’s real or not, as long as it’s a kick-ass song!”
The friends all laughed as they took another sip.

Diaspora eta Zu 2.0: A Discussion on New Technologies in the Diaspora
On Sunday, I was fortunate enough to appear on Benoit Etcheverry Macazaga‘s new radio program. Benoit has been a fixture in promoting Basque culture on the Internet for many years, hosting multiple radio programs dedicated to the Basques. His most recent venture, Diaspora eta Zu 2.0, is really focused on the Basque diaspora and connecting the diaspora with the motherland. I’ve “known” Benoit for many years, since the time he contributed an article in French on “le Rebot” (looking at that page, I realize I need to fix a lot of the accented script on my pages!!!). However, it was only this week, when he invited me to participate in Diaspora eta Zu 2.0, that I finally got to “meet” him face to face.

There were four guests on Sunday’s program, which focused on how new technologies impact the diaspora and the relationship with Basques in Euskal Herria. Frequent guest Esther Ciganda, who was born in the United States to two Basque immigrants but has returned to live in Euskal Herria, shared her experiences using the internet to interact with Basques all over the world. Alex Eguia, out of Mexico, runs EuskoBlog, a blog “from the diaspora for the diaspora.” Gonzalo Auza, who was the director of EuskoSare, a website and initiative that aspired to create a Global Basque Community (Gonzalo was one of the first, if not the first, person to use this phrase), joined from Argentina. And then, of course, there was me.
The premise of the shows was new technologies, and you can hear the entire program here. However, there were a few points I wanted to mention and potentially go into a little more deeply.
One topic was about the relationship of the diaspora to Basque culture. Esther made the excellent point that many Basques in the diaspora are more strongly connected to elements of Basque culture such as folk music and dancing than their contemporaries in the Basque Country itself. Many Basques in Euskal Herria respond to questions about if they can dance or if they enjoy folk music with a “meh.” For them, they don’t necessarily need these elements to feel a connection to their Basque culture, as they grow up being Basque. On the other hand, this is a relatively easy way for Basques in the diaspora to display their culture, to express their identity. Without other elements to hold on to, elements that are more challenging to develop such as language, these become very visible and expressive ways to highlight their culture. However, as noted by Alex, often this leads to myths that arise in the Basque diaspora, myths that become part of the diaspora’s culture but don’t necessarily resonate or have much to do with the culture as expressed in Euskal Herria. Myths that, for example, everyone dresses with a txapela, dances the jota, and plays the txistu.
Before, when my dad and people like him came over, and before, there was an influx of people from the Basque Country that brought their experiences with them, that helped informed what their children and the people around them knew about the Basque Country. My dad didn’t dance the jota, didn’t play the txistu, and rarely wore a txapela. But, he was Basque through-and-through and, just by being, he conveyed some aspect of the Basque Country. Now, however, as there is less incentive for people to emigrate from the Basque Country to places like the United States, that flux of people has dropped almost to zero, and that direct connection with the Basque Country has weakened. And, as pointed out by Esther, many in the diaspora never get a chance to visit Euskal Herria, the land of their ancestors, so never have a direct experience. On the other hand, Benoit noted how, even a hundred years ago, to have a cousin in the Americas or Australia was almost part of the definition of being Basque. The people of the Basque Country had a direction connection to the rest of the world through family. That connection is also being lost and, with it, some greater understanding of the rest of the world.
So where does that leave us? The literal ties that bind us together, the men and women that crossed the ocean looking for opportunity and a better life, are slowly disappearing and not being replaced. Both sides are weakened as those ties start to unravel. In the diaspora, as we grab onto dance and folk music as some tangible manifestation of that culture, we become more removed from the reality of the Basque Country. Euskal Herria is a modern, thriving country, pushing the state-of-the-art in science and technology and innovating in areas of gastronomy. It is a place where heavy metal and rap co-exist with folk music, where the serenity of the baserri stands next to the towering skyscapers and hulking Guggenheim. It is a place of contrasts, where certainly the folkloric elements exist and, in many cases, flourish, but where people are creating new industries and living lives that, day to day, focus on concerns other than these visible displays of Basque culture.
And, the people of the Basque Country lose that connection with the rest of the world. They start to lose those advocates that spoke so strongly for them around the world. They lose that base of talent and ideas that came from far away that only helped strengthen the society back home. And, they lose the sense of a global network, the type of interconnectedness that Gonzalo and EuskoSare tried to foster, in which there are Basques all over the world that, in their own little ways, support the Basques back in Euskal Herria.
These connections have another benefit. As discussed by Gonzalo, not everyone finds dance and music to be their preferred way to express their culture, their Basque identity, but in the diaspora, other modes of expressing that identity are lacking or difficult to develop. Dance and music are very visible ways of expressing culture that are relatively easily accessible. For those who aren’t into these things, there may almost be a sense that they aren’t as Basque as others. But, in the Basque Country itself, there are so many other ways one can be Basque. Having strong connections between Euskal Herria and the diaspora provide new opportunities — new modes — of cultural expression and provide for a richer landscape overall for all of us.
The theme of Sunday’s show was new technology and its role in the relationship between the diaspora and the Basques back in the Basque Country. I like to tell a story about my dad that highlights how I think technology might help. Of course, as noted by Alex, technology has its pitfalls, and there are dangers, such as the trolls that constantly arise out of the depths to plague any online community. However, in the long run, I believe technology will help us maintain, at least to some limited extent, the connections between Basques across the world.
When I was a kid, I didn’t know my dad’s family back in the Basque Country at all. He was the eldest of eight children and was the only one to leave Euskal Herria. The rest stayed behind, building lives and families in the homeland. My dad, first as a sheepherder and then as a truck driver, built what he could in the US. But, back then, it was expensive to travel, and the few times he did go back to Euskal Herria — literally less than five times in the first thirty years he lived in the US, typically for a wedding — he went alone. He called his family maybe once a year, around Christmas time, as the calls ended up costing so much. As a result, I had no connection at all with his family. I barely knew their names, I certainly didn’t know the names of their children. I didn’t meet my grandmother until I took my first trip over when I was twenty.
However, near the end of his life, my dad was on his cell phone constantly, talking with his brothers back in Euskal Herria. They talked seemingly daily, calls crossing the globe from both directions. He got to know his youngest brother, who had not been much more than a toddler when my dad left home. He got to know his nieces and nephews better. And, as a result, we all got to know them a bit more, we all got and shared news much more frequently and became just a bit more of a family than we had been before. I witnessed a real benefit to the new technologies that are so pervasive and, yes, in many cases disruptive to our lives. But, I also saw how they could help build new bridges between the Basque Country and the diaspora that might help us keep those connections alive. The materials might be different, but the bridges may yet survive and, hopefully, thrive.
Basque Fact of the Week: Selma Huxley Barkham, Basque-Canadian Historian
Today, it is well accepted that the Basques were early visitors to the coast of what would be known as North America. They established sites along the coast of what is now Newfoundland to process the whales they hunted and return the final product to Europe. With the local Native Americans, they created pidgin trading languages that surprised later European visitors. However, much of this history would be unknown to us if it wasn’t for one extremely dedicated, tenacious, and remarkable woman, Selma Huxley Barkham.

- Selma was born in 1927 in London. She came from a distinguished family. Her great-grandfather, Sir Henri-Gustave Joly de Lotbinière, had been the premier of Quebec and lieutenant-governor of British Columbia. Aldous Huxley, of Brave New World fame, was a cousin of her father. She spent some of her formative years in the United States when her father was stationed at the British Embassy in DC.
- In 1953, she met John Barkham, who she eventually married and together they moved to Ottawa. John was an architect and had done his thesis on the caserios or baserri in the Basque Country (though, this had not been his intention; he was forced to stay in the Basque Country due to an accident). Sadly, John died in 1964 (lymphatic cancer) and Selma, with four young children in tow, needed income. She became a historian of Canada and became interested in the early fishing voyages to Terra Nova, a thread she had originally picked up during an earlier visit to the Basque Country.
- Selma moved to the Basque town of Oñati, where she lived with her children for 20 years, delving deep into archives that had been untouched for centuries. She discovered literally thousands of documents that laid out the Basque history in Newfoundland, revealing that the Basques had not only been fishing cod in the area, but also hunting whales. She also discovered what were, at the time, the oldest civil documents written in Canada.
- In 1977, she led an archeological survey of Labrador during which the team discovered the remains of Basque whaling sites. The next year, another team, inspired by Selma’s work, discovered multiple shipwrecks and a cemetery. Together, these discoveries led to Red Bay being named a National Historic Site of Canada and, ultimately, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- For her work, Selma received many distinctions, including being the first woman to receive the Gold Medal of the Royal Canadian Geographical Society. She received an honorary doctorate from Memorial University in 1993. In 2014, she was recognized as a Lagun Onari of the Basque Country and, in 2018, she was awarded the Spanish Geographical Society’s International Prize
- Selma died on May 3, 2020 at the age of 93. Her son, Michael Barkham, has followed in her steps and has discovered an even older Canadian civil document, a will from 1563.
Primary source: “Enterprising researcher Selma Barkham rewrote a chapter of 16th-century history” by Joan Sullivan, in The Globe and Mail, published May 22, 2020.
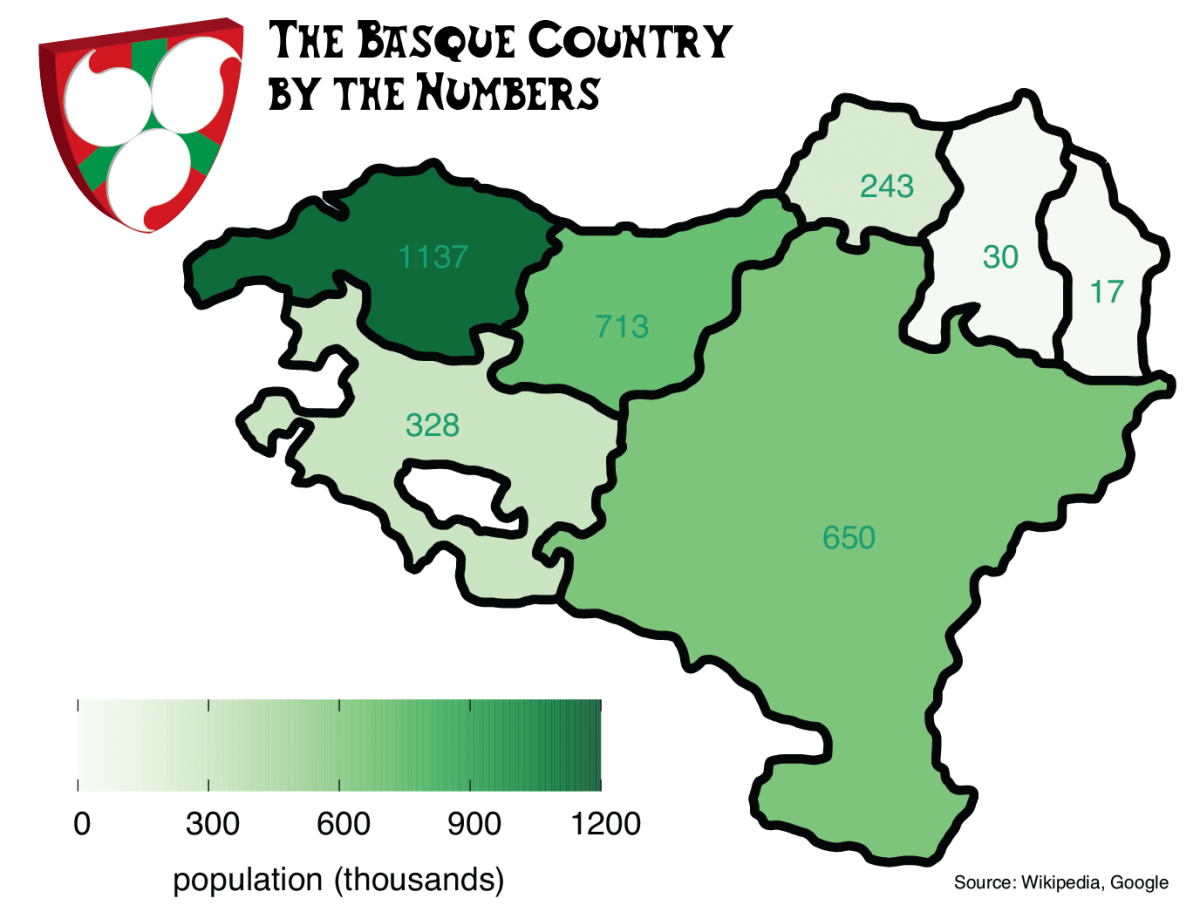
The Basque Country by the Numbers

The population of the Basque Country by province.

